The difference between first party and third party liability is essential to protecting a business properly. These differences are one of many aspects many business owners neglect far too frequently. Many business owners see insurance as a fixed cost. Others see it as some sort of tax. Considering some of the coverages are required by law in most states it is easy to understand why some business owners look at commercial insurance in this way. They are also part of your overall plan to protect the long term viability of your business. At the very least these policies should be. Protecting your business from both first party and third party liability is essential to properly protecting your business and here is an in-depth description of both types of coverage and why your business needs both.
![]()
The most basic example of the contrast between first and third party liability is in the two types of coverage most businesses purchase. These policies are Commercial Auto, Commercial Property, General Liability, and Workers Compensation. General Liability and Workers Compensation are common for all businesses because they are required by law for most businesses in most states. Commercial Auto and Property Coverage are common because many businesses own property and vehicles.
Commercial property, commercial auto, and workers compensation are examples of first party coverage because they cover damages to you and your business (ie damage to your vehicle, property, or employees). Another good example of first party coverage is a coverage like inland marine insurance. This coverage protects damage to your specialized equipment like a lawn mower or an expensive camera for a photographer.
General liability is an example of third party coverage because it protects your business from the liability your business faces to other people and organizations. In this case the liability would be to anyone damaged by the actions of your business. Third parties can include customers, vendor partners or anyone damaged by the actions of your business.
![]()
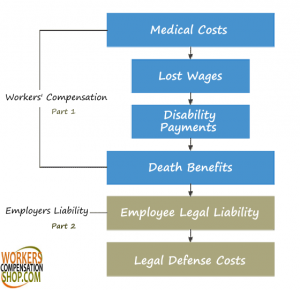
Workers’ Compensation and General Liability are required by law for most businesses in most states because they deal with the liability a business faces to both third parties and injured employees. If businesses chose not to secure these coverages and accidents occur, the only course of action for the victim would be to take the liable business to court. Because of these requirements they are frequently referred to as the ‘Exclusive Remedy’.
Other policies like those that cover a Data Breach are typically sold in tandem. Data Breach insurance is usually paired in combo as Cyber Security and Cyber Liability. Cyber Security, also commonly known as Privacy Notification and Crisis Management Expense Coverage, protects damage to you and your business that result from a data breach. These costs are commonly referred to as the ‘immediate response costs’. They could include, notifying all customers damaged by the breach, hiring a forensic expert to find the source of the breach, providing credit monitoring for those victims for up to one year (required by law in most states) and hiring a public relations firm to restore your businesses tainted image. Cyber Liability covers your liability to third parties. These third parties can include customers, vendors or anyone else damaged by your business as a result of the data breach.